Malaria

Malaria is an acute infectious disease caused by a protozoa “Plasmodium”.
Malaria is transmitted by the bite of female anopheles mosquito. Malaria is endemic to certain areas in India, especially in water bodies and in areas of poor sanitation. It is also endemic to certain African countries. People can get infected by malaria by travelling to the places and countries where it is highly prevalent. Hence, it is often considered as a cause of fever if the patient has undertaken a recent travel.
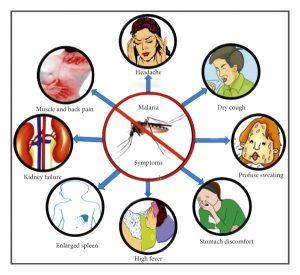
Symptoms
Malaria causes high grade fever, chills, rigors, headache, body pains, vomiting. Often, these symptoms are like the symptoms of other febrile illness like Dengue, typhoid, and other viral fever. However, malaria has severe shivering and intense sweating.
Malaria can cause complications
Malaria can cause severe illness in pregnant women and can cause complications like pre-term delivery and growth retardation in babies. Malaria can cause a severe and complicated infection leading to kidney, liver, lungs injury and anaemia and can lead to mortality. Sometimes, malaria can relapse in the same person after few months and years.
Report to your doctor early
Malaria is diagnosed by certain blood tests like smear examination and antigen tests in the blood. Most of the times, uncomplicated malaria does not require admission. However, admission is required if the patient is sick, has severe weakness and complications. There is an effective cure of Malaria, provided the patient presents to the hospital early and it is possible to prevent its complications and relapse. Drugs used in treatment of malaria are chloroquine, quinine, artesunate, artemether, lumefantrine, mefloquine. However, currently there is growing resistance to chloroquine. Hence, artemisinin-based combination therapies are recommended.

Prevention
Best way to combat malaria is its prevention. Control of breeding of mosquitoes and preventing mosquito bites is of paramount importance. Keep the surroundings of your home clean, avoid clogging of water, cover the drains to prevent breeding of mosquitos.
People who are planning to visit endemic places of malaria especially some of the African countries can take prophylactic medications to prevent malarial illness. These medications are generally started two weeks prior to the travel and continues up to four weeks after the travel. Currently, the vaccine used is prevention of malaria is still under development and not used routinely.
Use appropriate clothing to prevent bites, mosquito repellents as and when required. The malaria control programme and other Vector Borne Diseases namely Kala-azar, Dengue, Lymphatic Filariasis, Japanese Encephalitis and Chikungunya are integrated into the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) in 2002.
New tools for malaria prevention and control were introduced under NVBDCP i.e., monovalent Rapid Detection kits for P. falciparum detection in 2005; Artemisinin combination therapy in 2006; antigen detecting bi-valent RDTs for detection of both P. falciparum and P. vivax in 2013; and newer insecticides and larvicides in 2014- 15.
Being aware is vital. Early consultation with the doctor is necessary and this will facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
Associate Professor
General Medicine

